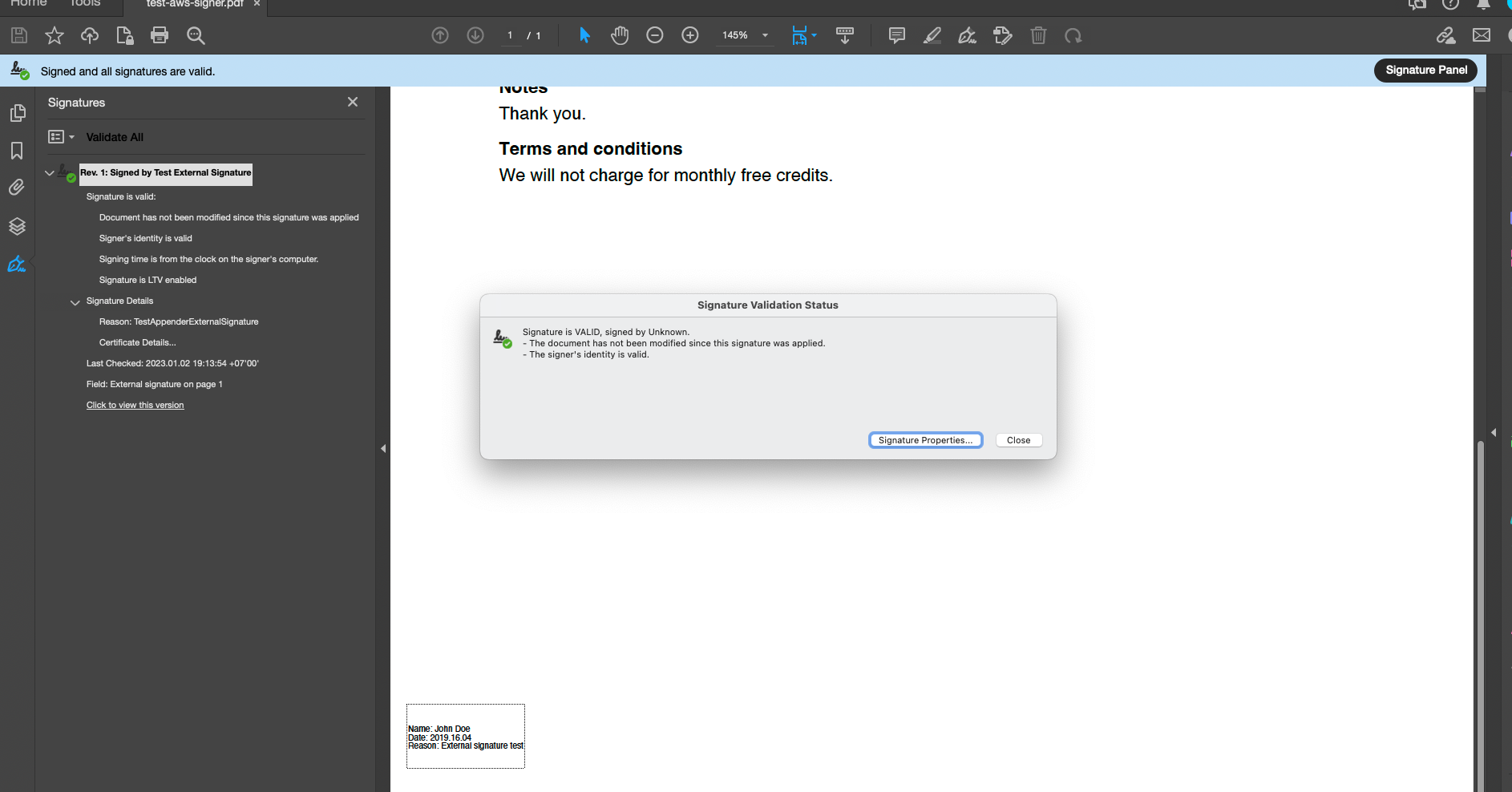
Sign PDF with UniPDF and Google Cloud KMS

Introduction
Previously we posted a guide regarding Sign PDF with UniPDF and AWS KMS.
Google Cloud KMS works similar like AWS KMS, where the difference is on the SDK being used and the steps involved in how to create the key for sign.
We still need to do a modification to the signing process of UniPDF in order to work with Google KMS Asymmetric Key.
Requirements
- Google Cloud KMS Key with purpose asymmetric sign and supported algorithm.
- Google Cloud KMS SDK https://github.com/googleapis/google-cloud-go/tree/main/kms
- UniPDF library https://github.com/unidoc/unipdf
The Process
Go to Google Cloud Console > Security > Key Management, then we create Key Ring and create a Key with purpose asymmetric sign under Key Ring and use the supported signature algorithm by Golang crypto.Signer.
Under this example we use 2048 bit RSA - PKCS#1 v1.5 padding - SHA256 digest as algorithm.
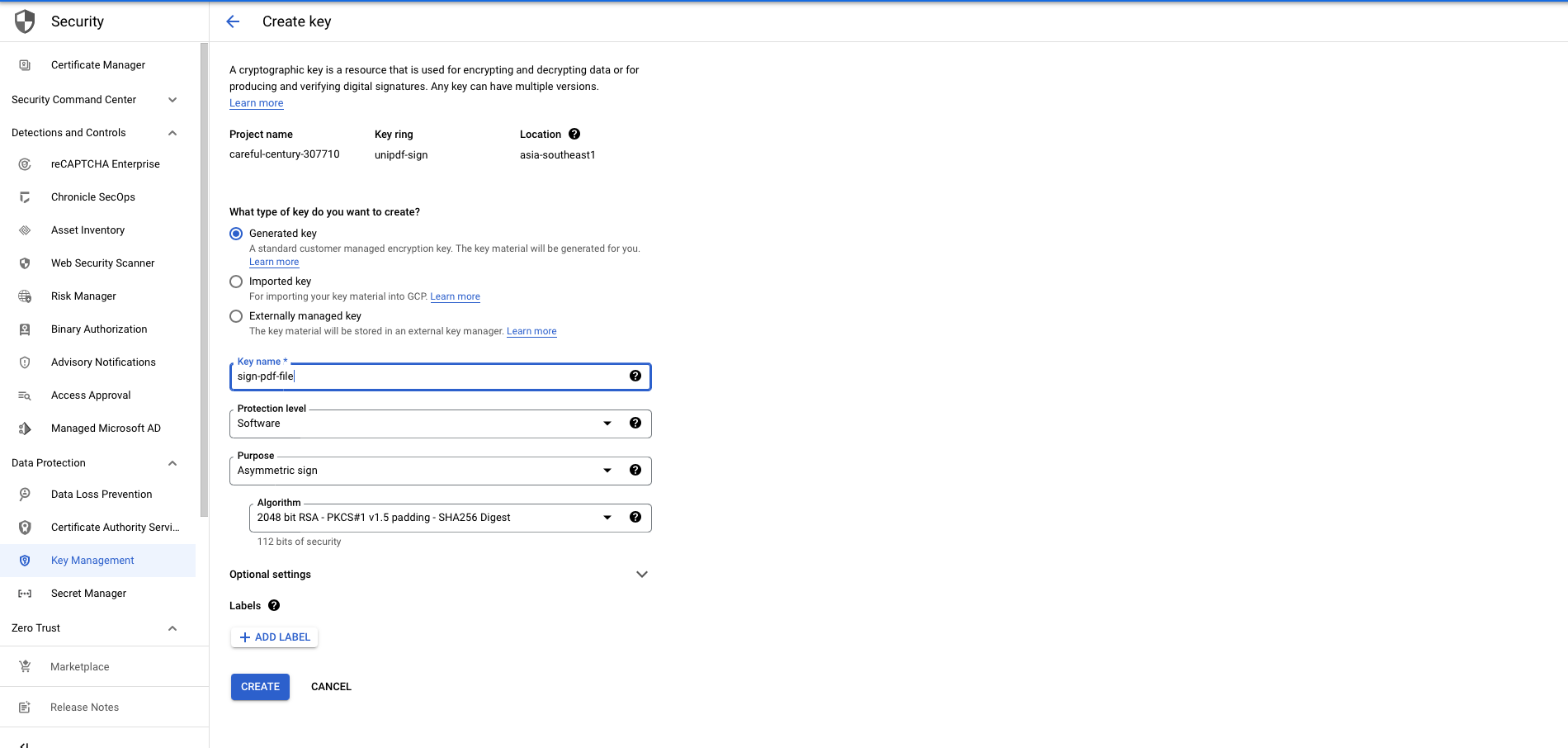
After creating the key, you will need to save the Key Name under this format projects/my-project/locations/us-east1/keyRings/my-key-ring/cryptoKeys/my-key/cryptoKeyVersions/123 for using it later to sign the PDF file.
You will need the public key associated with the key also, you can download it or get it using Google Cloud KMS API.
Now we modify the crypto.Signer in order to make self-signed certificate and sign it using Google Cloud KMS Key, you will need to create CSR for production and issuing the certificate to your CAs.
This part of code shows how to customize the crypto.Signer and use it with X509 to create a self-signed certificate.
// SignerCallback callback function of `crypto.Signer`
type SignerCallback func(rand io.Reader, digest []byte, opts crypto.SignerOpts) ([]byte, error)
// CryptoSigner Customize crypto signer wrapper to implement `crypto.Signer`.
type CryptoSigner struct {
keyName string
client \*kms.KeyManagementClient
callback SignerCallback
}
// EncryptionAlgorithmOID returns encryption OID algorithm supported by external services.
func (cs \*CryptoSigner) EncryptionAlgorithmOID() asn1.ObjectIdentifier {
return pkcs7.OIDEncryptionAlgorithmRSASHA256
}
// Public returns signer public key by calling to client services.
func (cs \*CryptoSigner) Public() crypto.PublicKey {
if cs.client == nil {
return nil
}
ctx := context.Background()
// Build the request.
req := &kmspb.GetPublicKeyRequest{
Name: cs.keyName,
}
// Call the API.
result, err := cs.client.GetPublicKey(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
return nil
}
// The 'Pem' field is the raw string representation of the public key.
// Convert 'Pem' into bytes for further processing.
key := []byte(result.Pem)
// Optional, but recommended: perform integrity verification on result.
// For more details on ensuring E2E in-transit integrity to and from Cloud KMS visit:
// https://cloud.google.com/kms/docs/data-integrity-guidelines
crc32c := func(data []byte) uint32 {
t := crc32.MakeTable(crc32.Castagnoli)
return crc32.Checksum(data, t)
}
if int64(crc32c(key)) != result.PemCrc32C.Value {
log.Fatal("getPublicKey: response corrupted in-transit")
return nil
}
// Optional - parse the public key. This transforms the string key into a Go
// PublicKey.
block, \_ := pem.Decode(key)
publicKey, err := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error: %v", err)
return nil
}
return publicKey
}
// Sign with customized `crypto.Signer`.
func (cs \*CryptoSigner) Sign(rand io.Reader, digest []byte, opts crypto.SignerOpts) (signature []byte, err error) {
if cs.callback != nil {
return cs.callback(rand, digest, opts)
}
ctx := context.Background()
// Sign the data.
// Optional but recommended: Compute digest's CRC32C.
crc32c := func(data []byte) uint32 {
t := crc32.MakeTable(crc32.Castagnoli)
return crc32.Checksum(data, t)
}
digestCRC32C := crc32c(digest)
// Build the signing request.
//
// Note: Key algorithms will require a varying hash function. For example,
// EC_SIGN_P384_SHA384 requires SHA-384.
req := &kmspb.AsymmetricSignRequest{
Name: cs.keyName,
Digest: &kmspb.Digest{
Digest: &kmspb.Digest_Sha256{
Sha256: digest,
},
},
DigestCrc32C: wrapperspb.Int64(int64(digestCRC32C)),
}
// Call the API.
result, err := cs.client.AsymmetricSign(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to sign digest: %v", err)
}
// Optional, but recommended: perform integrity verification on result.
// For more details on ensuring E2E in-transit integrity to and from Cloud KMS visit:
// https://cloud.google.com/kms/docs/data-integrity-guidelines
if !result.VerifiedDigestCrc32C {
return nil, errors.New("AsymmetricSign: request corrupted in-transit")
}
if int64(crc32c(result.Signature)) != result.SignatureCrc32C.Value {
return nil, errors.New("AsymmetricSign: response corrupted in-transit")
}
return result.Signature, nil
}
func NewCryptoSigner(c \*kms.KeyManagementClient, keyName string, cb SignerCallback) crypto.Signer {
return &CryptoSigner{
keyName: keyName,
client: c,
callback: cb,
}
}
...
// getExternalSignatureAndSign simulates an external service which signs the specified
// PDF file and returns its pdf signed bytes and signature.
func getExternalSignatureAndSign(inputPath, credPath, keyName string) ([]byte, []byte, error) {
gcKmsSign, err := GcKmsExternalSigner(credPath, keyName)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
defer gcKmsSign.client.Close()
now := time.Now()
// Initialize X509 certificate template.
template := x509.Certificate{
SerialNumber: new(big.Int),
Subject: pkix.Name{
CommonName: "UniDOC",
Organization: []string{"Test Company"},
},
NotBefore: now.Add(-time.Hour),
NotAfter: now.Add(time.Hour _ 24 _ 365),
PublicKeyAlgorithm: x509.RSA,
SignatureAlgorithm: x509.SHA256WithRSA,
KeyUsage: x509.KeyUsageDigitalSignature,
}
// We sign certificate using external signer that implement `crypto.Signer`.
certData, err := x509.CreateCertificate(rand.Reader, &template, &template, gcKmsSign.getPublicKey(), gcKmsSign.signer)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
cert, err := x509.ParseCertificate(certData)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
certChain := []*x509.Certificate{cert}
gcKmsSign.certChain = certChain
// Sign input file.
handler := gcKmsSign.toSigHandler()
pdfBytes, signature, err := generateSignedFile(inputPath, handler)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
return signature.Contents.Bytes(), pdfBytes, nil
}
- Initialize the UniPDF customized signature handler with the certificate and use Google Cloud KMS Sign to sign the digest message of PDF file.
This part of code shows how to create a customized model.SignatureHandler for external sign with Google Cloud KMS services.
// externalSigner is wrapper for third-party signer,
// needs to implement function of model.SignatureHandler.
// in this example, we use Google Cloud KMS as third-party signer.
type externalSigner struct {
certChain []*x509.Certificate
// keyName GC KMS ASYMMETRIC KEY_NAME.
keyName string
// client is third-party api client.
// We make client as interface for supporting another third-party signer.
client \*kms.KeyManagementClient
// signer customized `crypto.Signer`
signer crypto.Signer
ctx context.Context
}
// GcKmsExternalSigner wrap externalSigner to model.SignatureHandler.
// With this, you can implement any third-party client signer into signature handler.
func GcKmsExternalSigner(credPath, keyName string) (\*externalSigner, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
// Initiate Google Cloud KMS client.
client, err := kms.NewKeyManagementClient(ctx, gcOption.WithCredentialsFile(credPath))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Generate external `crypto.Singer`.
extSigner := NewCryptoSigner(client, keyName, nil)
return &externalSigner{
keyName: keyName,
client: client,
ctx: ctx,
signer: extSigner,
}, nil
}
// InitSignature sets the `model.PdfSignature` parameters.
func (es *externalSigner) InitSignature(sig *model.PdfSignature) error {
// Create PDF array object which will contain the certificate chain data.
pdfCerts := core.MakeArray()
for _, cert := range es.certChain {
pdfCerts.Append(core.MakeString(string(cert.Raw)))
}
// Append cert to signature.
sig.Cert = pdfCerts
handler := \*es
sig.Handler = &handler
sig.Filter = core.MakeName("Adobe.PPKLite")
sig.SubFilter = core.MakeName("adbe.pkcs7.detached")
sig.Reference = nil
digest, err := handler.NewDigest(sig)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return es.Sign(sig, digest)
}
// Sign return error on failed sign.
func (es *externalSigner) Sign(sig *model.PdfSignature, digest model.Hasher) error {
if digest == nil {
sig.Contents = core.MakeHexString(string(make([]byte, sigLen)))
return nil
}
buffer := digest.(\*bytes.Buffer)
signedData, err := pkcs7.NewSignedData(buffer.Bytes())
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Set digest algorithm which supported by Google Cloud KMS.
signedData.SetDigestAlgorithm(pkcs7.OIDDigestAlgorithmSHA256)
// Use customized callback if you want use different signature algorithm.
/* cb := func(rand io.Reader, digest []byte, opts crypto.SignerOpts) ([]byte, error) {
Sign digest.
ctx := context.Background()
// Sign the data.
// Optional but recommended: Compute digest's CRC32C.
crc32c := func(data []byte) uint32 {
t := crc32.MakeTable(crc32.Castagnoli)
return crc32.Checksum(data, t)
}
digestCRC32C := crc32c(digest)
// Build the signing request.
//
// Note: Key algorithms will require a varying hash function. For example,
// EC_SIGN_P384_SHA384 requires SHA-384.
req := &kmspb.AsymmetricSignRequest{
Name: cs.keyName,
Digest: &kmspb.Digest{
Digest: &kmspb.Digest_Sha256{
Sha256: digest,
},
},
DigestCrc32C: wrapperspb.Int64(int64(digestCRC32C)),
}
// Call the API.
result, err := cs.client.AsymmetricSign(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to sign digest: %v", err)
}
// Optional, but recommended: perform integrity verification on result.
// For more details on ensuring E2E in-transit integrity to and from Cloud KMS visit:
// https://cloud.google.com/kms/docs/data-integrity-guidelines
if !result.VerifiedDigestCrc32C {
return nil, erros.new("AsymmetricSign: request corrupted in-transit")
}
if int64(crc32c(result.Signature)) != result.SignatureCrc32C.Value {
return nil, errors.New("AsymmetricSign: response corrupted in-transit")
}
return result.Signature, nil
*/
siConfig := pkcs7.SignerInfoConfig{}
signer := es.signer
// If want to use customized callback for signature.
// signer = NewCryptoSigner(nil, "", cb)
// Add certificate to `signedData`.
err = signedData.AddSigner(es.certChain[0], signer, siConfig)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Call Detach() is you want to remove content from the signature
// and generate an S/MIME detached signature.
signedData.Detach()
// Finish() to obtain the signature bytes.
detachedSignature, err := signedData.Finish()
if err != nil {
return err
}
data := make([]byte, sigLen)
copy(data, detachedSignature)
sig.Contents = core.MakeHexString(string(data))
return nil
}
// IsApplicable returns true if the signature handler is applicable for the PdfSignature.
func (es *externalSigner) IsApplicable(sig *model.PdfSignature) bool {
if sig == nil || sig.Filter == nil || sig.SubFilter == nil {
return false
}
return (*sig.Filter == "Adobe.PPKMS" || *sig.Filter == "Adobe.PPKLite") && \*sig.SubFilter == "adbe.pkcs7.detached"
}
// NewDigest creates a new digest.
func (es *externalSigner) NewDigest(sig *model.PdfSignature) (model.Hasher, error) {
return bytes.NewBuffer(nil), nil
}
// Validate validates PdfSignature.
func (es *externalSigner) Validate(sig *model.PdfSignature, digest model.Hasher) (model.SignatureValidationResult, error) {
return model.SignatureValidationResult{
IsSigned: true,
IsVerified: true,
}, nil
}
// Returns signer public key by calling to singer services.
func (es \*externalSigner) getPublicKey() interface{} {
return es.signer.Public()
}
// toSigHandler cast `externalSigner` to `model.SignatureHandler`.
func (es \*externalSigner) toSigHandler() model.SignatureHandler {
return es
}
Complete Code Example
/*
- This example showcases how to digitally sign a PDF file using an external
- signing service Google Cloud KMS, you will need Google Cloud KMS KEY with `Asymmetric sign` Purpose.
-
- \$ ./pdf_sign_external_google_cloud_kms <INPUT_PDF_PATH> <OUTPUT_PDF_PATH> <GOOGLE_CLOUD_CREDENTIALS_PATH> <KEY_NAME>
-
- <KEY_NAME> format example: projects/my-project/locations/us-east1/keyRings/my-key-ring/cryptoKeys/my-key/cryptoKeyVersions/123
*/
package main
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"crypto"
"crypto/rand"
"crypto/x509"
"crypto/x509/pkix"
"encoding/asn1"
"encoding/pem"
"errors"
"fmt"
"hash/crc32"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"math/big"
"os"
"time"
kms "cloud.google.com/go/kms/apiv1"
gcOption "google.golang.org/api/option"
kmspb "google.golang.org/genproto/googleapis/cloud/kms/v1"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/types/known/wrapperspb"
"github.com/unidoc/pkcs7"
"github.com/unidoc/unipdf/v3/annotator"
"github.com/unidoc/unipdf/v3/common/license"
"github.com/unidoc/unipdf/v3/core"
"github.com/unidoc/unipdf/v3/model"
"github.com/unidoc/unipdf/v3/model/sighandler"
)
func init() {
// Make sure to load your metered License API key prior to using the library.
// If you need a key, you can sign up and create a free one at https://cloud.unidoc.io
err := license.SetMeteredKey(os.Getenv(`UNIDOC_LICENSE_API_KEY`))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
var (
now = time.Now()
// sigLen signature length.
sigLen = 8192
)
const usagef = "Usage: %s INPUT_PDF_PATH OUTPUT_PDF_PATH GOOGLE_CLOUD_CREDENTIALS_PATH KEY_NAME\n"
func main() {
args := os.Args
if len(args) < 5 {
fmt.Printf(usagef, os.Args[0])
return
}
inputPath := args[1]
outputPath := args[2]
gcCredentialsPath := args[3]
keyName := args[4]
// Generate PDF file signed with empty signature.
handler, err := sighandler.NewEmptyAdobePKCS7Detached(sigLen)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Fail: %v\n", err)
}
\_, signature, err := generateSignedFile(inputPath, handler)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Fail: %v\n", err)
}
// Parse signature byte range.
byteRange, err := parseByteRange(signature.ByteRange)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Fail: %v\n", err)
}
// This would be the time to send the PDF buffer to a signing device or
// signing web service and get back the signature. We will simulate this by
// signing the PDF using UniDoc and returning the signature data.
signatureData, pdfData, err := getExternalSignatureAndSign(inputPath, gcCredentialsPath, keyName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Fail: %v\n", err)
}
// Apply external signature to the PDF data buffer.
// Overwrite the generated empty signature with the signature
// bytes retrieved from the external service.
sigBytes := make([]byte, sigLen)
copy(sigBytes, signatureData)
sig := core.MakeHexString(string(sigBytes)).WriteString()
copy(pdfData[byteRange[1]:byteRange[2]], []byte(sig))
// Write output file.
if err := ioutil.WriteFile(outputPath, pdfData, os.ModePerm); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Fail: %v\n", err)
}
log.Printf("PDF file successfully signed. Output path: %s\n", outputPath)
}
// generateSignedFile generates a signed version of the input PDF file using the
// specified signature handler.
func generateSignedFile(inputPath string, handler model.SignatureHandler) ([]byte, \*model.PdfSignature, error) {
// Create reader.
file, err := os.Open(inputPath)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
defer file.Close()
reader, err := model.NewPdfReader(file)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
// Create appender.
appender, err := model.NewPdfAppender(reader)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
// Create signature.
signature := model.NewPdfSignature(handler)
signature.SetName("GOOGLECLOUD KMS Sign")
signature.SetReason("TestGCKMSSignature")
signature.SetDate(now, "")
if err := signature.Initialize(); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
// Create signature field and appearance.
opts := annotator.NewSignatureFieldOpts()
opts.FontSize = 10
opts.Rect = []float64{10, 25, 75, 60}
field, err := annotator.NewSignatureField(
signature,
[]*annotator.SignatureLine{
annotator.NewSignatureLine("Name", "John Doe"),
annotator.NewSignatureLine("Date", "2023.01.01"),
annotator.NewSignatureLine("Reason", "GC KMS Sing Test"),
},
opts,
)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
field.T = core.MakeString("External signature")
if err = appender.Sign(1, field); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
// Write PDF file to buffer.
pdfBuf := bytes.NewBuffer(nil)
if err = appender.Write(pdfBuf); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
return pdfBuf.Bytes(), signature, nil
}
// getExternalSignatureAndSign simulates an external service which signs the specified
// PDF file and returns its pdf signed bytes and signature.
func getExternalSignatureAndSign(inputPath, credPath, keyName string) ([]byte, []byte, error) {
gcKmsSign, err := GcKmsExternalSigner(credPath, keyName)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
defer gcKmsSign.client.Close()
now := time.Now()
// Initialize X509 certificate template.
template := x509.Certificate{
SerialNumber: new(big.Int),
Subject: pkix.Name{
CommonName: "UniDOC",
Organization: []string{"Test Company"},
},
NotBefore: now.Add(-time.Hour),
NotAfter: now.Add(time.Hour _ 24 _ 365),
PublicKeyAlgorithm: x509.RSA,
SignatureAlgorithm: x509.SHA256WithRSA,
KeyUsage: x509.KeyUsageDigitalSignature,
}
// We sign certificate using external signer that implement `crypto.Signer`.
certData, err := x509.CreateCertificate(rand.Reader, &template, &template, gcKmsSign.getPublicKey(), gcKmsSign.signer)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
cert, err := x509.ParseCertificate(certData)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
certChain := []*x509.Certificate{cert}
gcKmsSign.certChain = certChain
// Sign input file.
handler := gcKmsSign.toSigHandler()
pdfBytes, signature, err := generateSignedFile(inputPath, handler)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
return signature.Contents.Bytes(), pdfBytes, nil
}
// parseByteRange parses the ByteRange value of the signature field.
func parseByteRange(byteRange \*core.PdfObjectArray) ([]int64, error) {
if byteRange == nil {
return nil, errors.New("byte range cannot be nil")
}
if byteRange.Len() != 4 {
return nil, errors.New("invalid byte range length")
}
s1, err := core.GetNumberAsInt64(byteRange.Get(0))
if err != nil {
return nil, errors.New("invalid byte range value")
}
l1, err := core.GetNumberAsInt64(byteRange.Get(1))
if err != nil {
return nil, errors.New("invalid byte range value")
}
s2, err := core.GetNumberAsInt64(byteRange.Get(2))
if err != nil {
return nil, errors.New("invalid byte range value")
}
l2, err := core.GetNumberAsInt64(byteRange.Get(3))
if err != nil {
return nil, errors.New("invalid byte range value")
}
return []int64{s1, s1 + l1, s2, s2 + l2}, nil
}
// SignerCallback callback function of `crypto.Signer`
type SignerCallback func(rand io.Reader, digest []byte, opts crypto.SignerOpts) ([]byte, error)
// CryptoSigner Customize crypto signer wrapper to implement `crypto.Signer`.
type CryptoSigner struct {
keyName string
client \*kms.KeyManagementClient
callback SignerCallback
}
// EncryptionAlgorithmOID returns encryption OID algorithm supported by external services.
func (cs \*CryptoSigner) EncryptionAlgorithmOID() asn1.ObjectIdentifier {
return pkcs7.OIDEncryptionAlgorithmRSASHA256
}
// Public returns signer public key by calling to client services.
func (cs \*CryptoSigner) Public() crypto.PublicKey {
if cs.client == nil {
return nil
}
ctx := context.Background()
// Build the request.
req := &kmspb.GetPublicKeyRequest{
Name: cs.keyName,
}
// Call the API.
result, err := cs.client.GetPublicKey(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
return nil
}
// The 'Pem' field is the raw string representation of the public key.
// Convert 'Pem' into bytes for further processing.
key := []byte(result.Pem)
// Optional, but recommended: perform integrity verification on result.
// For more details on ensuring E2E in-transit integrity to and from Cloud KMS visit:
// https://cloud.google.com/kms/docs/data-integrity-guidelines
crc32c := func(data []byte) uint32 {
t := crc32.MakeTable(crc32.Castagnoli)
return crc32.Checksum(data, t)
}
if int64(crc32c(key)) != result.PemCrc32C.Value {
log.Fatal("getPublicKey: response corrupted in-transit")
return nil
}
// Optional - parse the public key. This transforms the string key into a Go
// PublicKey.
block, \_ := pem.Decode(key)
publicKey, err := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error: %v", err)
return nil
}
return publicKey
}
// Sign with customized `crypto.Signer`.
func (cs \*CryptoSigner) Sign(rand io.Reader, digest []byte, opts crypto.SignerOpts) (signature []byte, err error) {
if cs.callback != nil {
return cs.callback(rand, digest, opts)
}
ctx := context.Background()
// Sign the data.
// Optional but recommended: Compute digest's CRC32C.
crc32c := func(data []byte) uint32 {
t := crc32.MakeTable(crc32.Castagnoli)
return crc32.Checksum(data, t)
}
digestCRC32C := crc32c(digest)
// Build the signing request.
//
// Note: Key algorithms will require a varying hash function. For example,
// EC_SIGN_P384_SHA384 requires SHA-384.
req := &kmspb.AsymmetricSignRequest{
Name: cs.keyName,
Digest: &kmspb.Digest{
Digest: &kmspb.Digest_Sha256{
Sha256: digest,
},
},
DigestCrc32C: wrapperspb.Int64(int64(digestCRC32C)),
}
// Call the API.
result, err := cs.client.AsymmetricSign(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to sign digest: %v", err)
}
// Optional, but recommended: perform integrity verification on result.
// For more details on ensuring E2E in-transit integrity to and from Cloud KMS visit:
// https://cloud.google.com/kms/docs/data-integrity-guidelines
if !result.VerifiedDigestCrc32C {
return nil, errors.New("AsymmetricSign: request corrupted in-transit")
}
if int64(crc32c(result.Signature)) != result.SignatureCrc32C.Value {
return nil, errors.New("AsymmetricSign: response corrupted in-transit")
}
return result.Signature, nil
}
func NewCryptoSigner(c \*kms.KeyManagementClient, keyName string, cb SignerCallback) crypto.Signer {
return &CryptoSigner{
keyName: keyName,
client: c,
callback: cb,
}
}
// externalSigner is wrapper for third-party signer,
// needs to implement function of model.SignatureHandler.
// in this example, we use Google Cloud KMS as third-party signer.
type externalSigner struct {
certChain []*x509.Certificate
// keyName GC KMS ASYMMETRIC KEY_NAME.
keyName string
// client is third-party api client.
// We make client as interface for supporting another third-party signer.
client \*kms.KeyManagementClient
// signer customized `crypto.Signer`
signer crypto.Signer
ctx context.Context
}
// GcKmsExternalSigner wrap externalSigner to model.SignatureHandler.
// With this, you can implement any third-party client signer into signature handler.
func GcKmsExternalSigner(credPath, keyName string) (\*externalSigner, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
// Initiate Google Cloud KMS client.
client, err := kms.NewKeyManagementClient(ctx, gcOption.WithCredentialsFile(credPath))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Generate external `crypto.Singer`.
extSigner := NewCryptoSigner(client, keyName, nil)
return &externalSigner{
keyName: keyName,
client: client,
ctx: ctx,
signer: extSigner,
}, nil
}
// InitSignature sets the `model.PdfSignature` parameters.
func (es *externalSigner) InitSignature(sig *model.PdfSignature) error {
// Create PDF array object which will contain the certificate chain data.
pdfCerts := core.MakeArray()
for _, cert := range es.certChain {
pdfCerts.Append(core.MakeString(string(cert.Raw)))
}
// Append cert to signature.
sig.Cert = pdfCerts
handler := \*es
sig.Handler = &handler
sig.Filter = core.MakeName("Adobe.PPKLite")
sig.SubFilter = core.MakeName("adbe.pkcs7.detached")
sig.Reference = nil
digest, err := handler.NewDigest(sig)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return es.Sign(sig, digest)
}
// Sign return error on failed sign.
func (es *externalSigner) Sign(sig *model.PdfSignature, digest model.Hasher) error {
if digest == nil {
sig.Contents = core.MakeHexString(string(make([]byte, sigLen)))
return nil
}
buffer := digest.(\*bytes.Buffer)
signedData, err := pkcs7.NewSignedData(buffer.Bytes())
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Set digest algorithm which supported by Google Cloud KMS.
signedData.SetDigestAlgorithm(pkcs7.OIDDigestAlgorithmSHA256)
// Use customized callback if you want use different signature algorithm.
/* cb := func(rand io.Reader, digest []byte, opts crypto.SignerOpts) ([]byte, error) {
Sign digest.
ctx := context.Background()
// Sign the data.
// Optional but recommended: Compute digest's CRC32C.
crc32c := func(data []byte) uint32 {
t := crc32.MakeTable(crc32.Castagnoli)
return crc32.Checksum(data, t)
}
digestCRC32C := crc32c(digest)
// Build the signing request.
//
// Note: Key algorithms will require a varying hash function. For example,
// EC_SIGN_P384_SHA384 requires SHA-384.
req := &kmspb.AsymmetricSignRequest{
Name: cs.keyName,
Digest: &kmspb.Digest{
Digest: &kmspb.Digest_Sha256{
Sha256: digest,
},
},
DigestCrc32C: wrapperspb.Int64(int64(digestCRC32C)),
}
// Call the API.
result, err := cs.client.AsymmetricSign(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to sign digest: %v", err)
}
// Optional, but recommended: perform integrity verification on result.
// For more details on ensuring E2E in-transit integrity to and from Cloud KMS visit:
// https://cloud.google.com/kms/docs/data-integrity-guidelines
if !result.VerifiedDigestCrc32C {
return nil, erros.new("AsymmetricSign: request corrupted in-transit")
}
if int64(crc32c(result.Signature)) != result.SignatureCrc32C.Value {
return nil, errors.New("AsymmetricSign: response corrupted in-transit")
}
return result.Signature, nil
*/
siConfig := pkcs7.SignerInfoConfig{}
signer := es.signer
// If want to use customized callback for signature.
// signer = NewCryptoSigner(nil, "", cb)
// Add certificate to `signedData`.
err = signedData.AddSigner(es.certChain[0], signer, siConfig)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Call Detach() is you want to remove content from the signature
// and generate an S/MIME detached signature.
signedData.Detach()
// Finish() to obtain the signature bytes.
detachedSignature, err := signedData.Finish()
if err != nil {
return err
}
data := make([]byte, sigLen)
copy(data, detachedSignature)
sig.Contents = core.MakeHexString(string(data))
return nil
}
// IsApplicable returns true if the signature handler is applicable for the PdfSignature.
func (es *externalSigner) IsApplicable(sig *model.PdfSignature) bool {
if sig == nil || sig.Filter == nil || sig.SubFilter == nil {
return false
}
return (*sig.Filter == "Adobe.PPKMS" || *sig.Filter == "Adobe.PPKLite") && \*sig.SubFilter == "adbe.pkcs7.detached"
}
// NewDigest creates a new digest.
func (es *externalSigner) NewDigest(sig *model.PdfSignature) (model.Hasher, error) {
return bytes.NewBuffer(nil), nil
}
// Validate validates PdfSignature.
func (es *externalSigner) Validate(sig *model.PdfSignature, digest model.Hasher) (model.SignatureValidationResult, error) {
return model.SignatureValidationResult{
IsSigned: true,
IsVerified: true,
}, nil
}
// Returns signer public key by calling to singer services.
func (es \*externalSigner) getPublicKey() interface{} {
return es.signer.Public()
}
// toSigHandler cast `externalSigner` to `model.SignatureHandler`.
func (es \*externalSigner) toSigHandler() model.SignatureHandler {
return es
}
Conclusion
In this article we have shown how to use UniPDF to sign with GCP KMS. Google Cloud KMS works simila to how signing with AWS KMS works, where the differences are with the key creation and how to use the SDK’s to get the public key and sign the digest message. If you have any questions, don’t hesitate to contact us and we will be happy to help!